By: Leah Stokes & Noelle Selin
Mercury is a toxin that harms human health. People become exposed to mercury primarily by eating fish. In some communities, where artisanal and small-scale gold mining (ASGM) occurs, exposure can be quite high. This is because people may breathe in mercury fumes from the process.
It is possible to tell how much mercury a person has been exposed to by testing their hair, blood and urine. Estimating mercury exposure through hair samples is primarily a measure of methylmercury — the most toxic form of mercury. But, it may also be influenced by the hair surface’s exposure to emissions. For example, if a person using mercury to capture gold stands over the amalgam (the mixture of mercury and gold) while they are burning off the mercury, it is likely that some of this mercury could end up on their hair.
At INC2, the second round of the mercury treaty negotiations in Chiba, Japan in early 2011, delegates and observers were able to measure the mercury concentration in their hair. We both sent in samples, and found out that Noelle had a concentration of 1.39 ppm while Leah had a concentration of 0.75 ppm. These values are close to, or below the WHO and the US EPA guidance values for mercury in hair: 1.8 ppm and 1.2 ppm respectively.* Many other delegates at the negotiations had mercury concentrations around 4.00 ppm, which is above these guidance values. For most people, mercury concentrations in hair reflect fish consumption, and Leah is mostly a vegetarian, while Noelle is from New England and loves fish.
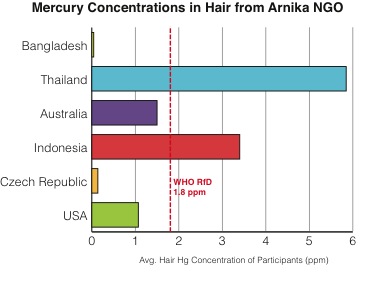
Chart complied by Amanda Giang and Julie van der Hoop using self-reported data on Arnika’s website.
Arnika, a Czech non-governmental organization (NGO), and a member of both International POPs Elimination Network (IPEN) and Zero Mercury Working Group (ZMWG), has posted a website where people around the world are reporting the mercury concentrations in their hair. These individuals then reflect on this information in light of the current negotiations, sending a message to delegates.
Amanda Giang and Julie van der Hoop compiled the self-reported data from Arnika’s website, to give you a sense of how mercury concentrations in hair can vary across countries.
* Note: The WHO and EPA actually give their recommendations in terms of daily oral intake of methylmercury. Amanda Giang converted these values to hair mercury concentrations using conversion factors developed by Rice et al. (2010), Stern (2005), and Allen et al. (2007).
